Something happened in the early 2000s that forever changed the entire business landscape. This change was mainly felt across the customer service industry, but soon, many other industries caught on to this wave.
Before this particular tech, customer service was slow, required massive workforce power, and was extremely expensive.
Then, NLP (Natural Language Processing) and chatbots changed everything.
Although the first NLP and chatbots became “alive” in the 1960s, they were bad at truly understanding human language and intent, providing rigid, impersonal, and often wrong data.
But in the early 2000s, NLP advancements transformed chatbots. NLP enabled a better understanding of human language, enhancing chatbots’ effectiveness in customer service. This breakthrough allowed them to grasp context and provide personalized, human-like responses. As a result, businesses have started to use chatbots widely to provide 24/7 customer service, making it much better and cutting costs.
This massive shift in customer service technology is similar to recent improvements in using Natural Language Processing in search engines.
Key Takeaways:
- Natural Language Processing in search engines vastly improves performance and user experience.
- NLP techniques transform ambiguous text into actionable data.
- NLP and AI in search technology are crucial for semantic search, ensuring relevant and accurate results.
- NLP enables natural language search engines to better understand human language.
Understanding Natural Language Processing in Search Engines
NLP enhances search engine’s ability to understand human language. Integrating NLP into search engine algorithms is vital to improving performance and user experience.
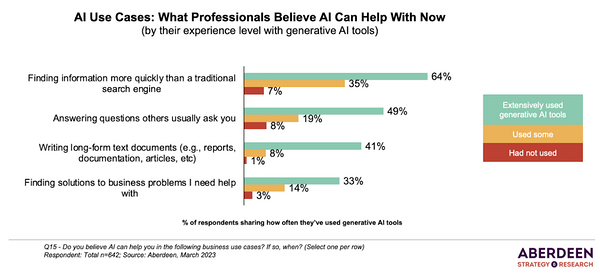
According to a recent Aberdeen research, 64% of businesses believe that NLP and AI-powered search is better at finding relevant data more quickly and efficiently than traditional search engines.
In October 2019, something quite important happened. Google made understanding of natural language in search much more relevant with their BERT update:
“At its core, Search is about understanding language. It’s our job to figure out what you’re searching for and surface helpful information from the web, no matter how you spell or combine the words in your query.
While we’ve continued to improve our language understanding capabilities over the years, we sometimes still don’t quite get it right, particularly with complex or conversational queries. In fact, that’s one of the reasons why people often use “keyword-ese,” typing strings of words that they think we’ll understand, but aren’t actually how they’d naturally ask a question.”
It’s all about making the process as natural and as effective as possible.
Fundamentals of NLP in Search Technology
NLP operates at the core of modern search engines. You basically cannot separate the two anymore, as together, they bridge human language and machine understanding.
This technology helps search engines better analyze user queries because they interpret search queries, recognize keywords, and understand natural language nuances.
How NLP Processes Queries and Uses Semantic Search
Imagine Natural Language Processing in search engine technology as a librarian who not only understands the specific words in a book but also gets the context, nuances, and relationships between those words.
With traditional search engine tech, it’s like asking a librarian for a book on how plants grow, and the librarian merely gives you a list of books containing the exact phrase how plants grow.
Now, with NLP, it’s like having a highly intelligent librarian who not only considers the literal words but also understands the meaning and intent behind your query.
If you ask the NLP-powered search engine about “information on the process of plants growing,” it includes related terms and correctly interprets why you are searching for it. It provides more accurate and relevant results, even if the exact words in your query don’t match the content it’s searching through.

NLP processes human language and transforms text into actionable data. It understands the nuances of human language, even to the point of slang and indirect meanings.
With the power of AI-powered semantic search, sophisticated language models and machine learning, you only get relevant and accurate results.
It’s like having a close buddy who knows you really well.
Critical Benefits of Natural Language Processing in Search Engines
Natural Language Processing (NLP) significantly improves search engines in multiple ways, enhancing user experience and efficiency.
Enhancing User Experience through Accurate Results
NLP ensures accurate and relevant search results, understands search queries better, and improves and learns from search experience. This empowers users to interact with search engines like they would talk to a friend or colleague, mirroring real-life human communication.
NLP and AI boost user and customer experience for modern businesses, helping them build better customer relationships.
Improved Search Efficiency for Voice and Visual Search
By recognizing and understanding context and intent in complex queries, NLP and AI in search technology are crucial for voice and visual search.
This has proven critical in, for example, the e-commerce industry, as it perfects personalization and uses search history to better optimize future searches and actually tailor results to individual needs.
NLP and Voice Search
NLP interprets spoken queries accurately and enables search engines like Google or Bing to analyze and process spoken queries with top-level accuracy, allowing seamless interaction through conversational language.
NLP-powered AI search engine provides users the freedom to seek knowledge as simply as asking a question out loud.
NLP and AI-Powered Visual Search
While NLP doesn’t play a key role in visual AI search tech, it does help make visual search more accurate, comprehensive, and user-friendly.
For example, in a photo search application, users might provide search queries in natural language text. In such cases, NLP can be used to better understand the user’s intent expressed in the text query, and then the system can leverage visual AI to retrieve relevant visual content based on that understanding.
Predictions for NLP’s Evolution in Search Engines
The future of NLP in search engines is set to overcome challenges and bring advancements. Integrating Natural Language Processing with AI in search technology will become more advanced, improving the understanding of user intent.
Expanding the knowledge graph is key for the evolution of this highly potent tech. This enhancement will enable search engines to provide even more precise, context-aware results, empowering digital assistants to offer unbeatable advantages.
This is why we have bad news for businesses that don’t use AI and NLP-based tech. It’s why search engine optimization strategies and modern companies must adapt to these new trends, ensuring visibility and improving customer experience in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Upgrade Your E-Commerce Search With Visual AI Tool
Miros.ai helps e-commerce businesses provide visitors with a quick and vastly improved shopping experience. It helps them find exactly the product they want in under 60 seconds.
This product discovery tool uses visual AI technology to understand what’s in a product photo and uses wordless search to provide the customer with a whole wall of products that are relevant to the shopper’s intent, making their buying journey shorter.
The customer can input none or maybe one text-based search and then, by tapping the products they like, get a personalized feed of similar products that perfectly fit their needs and wants.
You can see an example of it here:
Miros’ ecommerce clients quickly experience major boosts in conversion rate and other KPIs like AOV, Visitor Retention and GMV. At the same time, the shop visitors who make purchases through the Miros tool bring in 2.6x more revenue per shopper than the control group.
Let’s deliver similar KPI boosts for your business. Book a quick demo here and see how Miros can help you embrace the future of search engines.




